What does ‘enterprise-grade software’ really mean?

In today’s digital world, the term “enterprise-grade software” is a buzzword that’s thrown around without a clear understanding of what it means. While many organizations recognize the importance of robust software for their business, distinguishing between standard software and truly enterprise-grade solutions is a challenge. Understanding this distinction is crucial for businesses seeking scalable, secure, and efficient systems that can support their growth and complex operational requirements.
Unlike consumer software, it’s built to handle mission-critical operations while meeting strict requirements for security, scalability and integration. For these solutions, enterprise grade means ensuring that end users can efficiently and securely perform their work while maintaining compliance within the organization. Enterprise organizations, in particular, benefit from these capabilities as they require software that supports large-scale, complex, and regulated environments. As global software spending is over $1 trillion annually with 12% year-over-year growth, understanding this category is crucial for modern business leaders.
What is enterprise-grade software
Enterprise-grade software is applications designed to meet the complex, large-scale needs of businesses and organizations, not individual users. While general computer software may address basic or personal requirements, enterprise-grade solutions — often referred to as enterprise applications — are built with robustness, scalability, security and seamless integration into existing business infrastructure as core principles.
At its core, enterprise-grade software is about performing under extreme demands while maintaining the reliability and security standards that large organizations require. The software must handle large user loads, process massive amounts of data, and integrate with multiple existing systems without compromising performance or security.
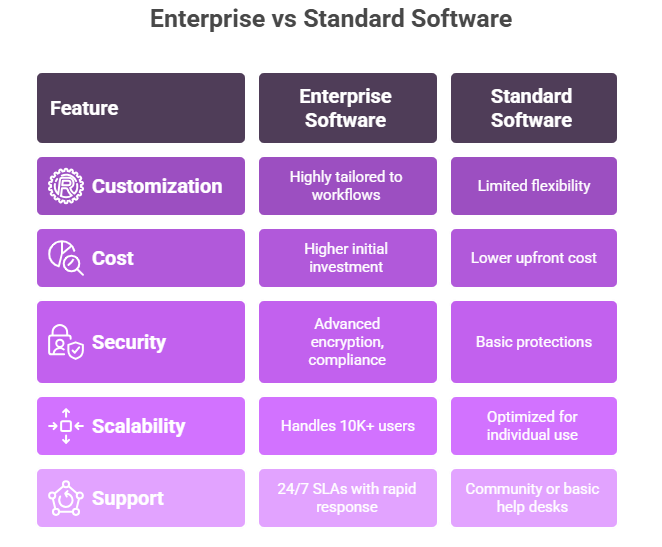
Characteristics of enterprise-grade software
Comprehensive security and compliance
Enterprise-grade software puts security as a fundamental requirement not an afterthought. This includes end-to-end encryption, data loss prevention and compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA and SOC 2. Data protection is a key aspect of enterprise software security, ensuring compliance and safeguarding sensitive information against unauthorized access or breaches. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach 2024 report, the average cost of a data breach was $4.88 million, so robust security measures are not just important but financially critical for organizations.
Security features in enterprise software include:
- multi-factor authentication and role-based access control,
- data security measures such as advanced encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit, and adherence to regulatory requirements,
- regular security audits and penetration testing,
- compliance monitoring and reporting capabilities.
Security protocols must also extend to data storage, ensuring that all stored information is protected and compliant with relevant regulations.
Scalability and performance
One of the key characteristics of enterprise-grade software is its ability to scale seamlessly as the organization grows. This scaling happens in multiple dimensions: vertical, horizontal and beyond:
User scalability: The software must handle hundreds or thousands of concurrent users without performance degradation. Research shows that scalable platforms can achieve uptime rates of 99.9% compared to 95% for standard systems.
Data scalability: Enterprise systems must process and store massive amounts of data efficiently. In enterprise environments, scalability means multiple dimensions: data volume scalability (handling growing datasets), transaction scalability (processing higher transaction rates) and geographical scalability (supporting global operations).
Infrastructure scalability: The ability to distribute workloads across multiple servers and leverage cloud infrastructure for resource allocation. Utilizing a cloud platform provides scalable and secure solutions for a wide range of enterprise needs, such as data storage, computing power, and integration with other enterprise tools. Cloud based software enables accessibility and scalability, allowing remote access, real-time updates, and seamless collaboration.
Integration capabilities
Enterprise-grade software must integrate with existing business systems including PLM, ERP, CRM, HRM platforms, and management software that automates core business functions. This integration is supported by robust operating systems, which serve as foundational software to ensure compatibility and smooth operation with various enterprise applications. Such integration minimizes disruption during implementation and ensures a cohesive IT infrastructure that supports end-to-end business processes.
Statistics show that businesses using APIs for integration see a 61% increase in competitive advantage, so integration is key in enterprise environments.
Support and maintenance
Unlike consumer software, enterprise-grade solutions require continuous professional support, regular updates and proactive maintenance. Professional services play a crucial role by providing expert guidance and ongoing technical assistance to ensure the effective implementation, integration, and optimization of enterprise software. This includes:
- 24/7 technical support with dedicated account management,
- regular security patches and system updates,
- performance optimization and monitoring,
- disaster recovery and backup solutions.
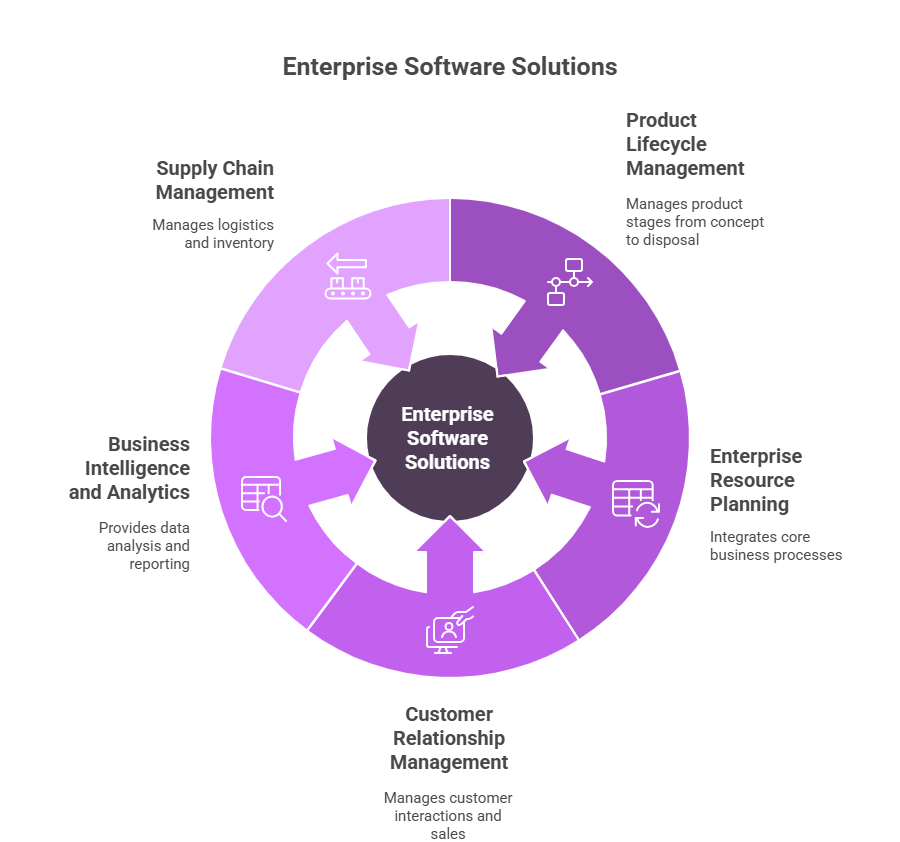
Examples of enterprise software solutions
Product lifecycle management (PLM)
It is an enterprise software system that manages various business processes involved in every stage of a product’s life – from initial concept and design, through manufacturing and service, to end-of-life and disposal. PLM solutions centralize product data, streamline collaboration and ensure compliance, so it’s a classic example of enterprise-grade software.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems
ERP systems, also known as ERP software, are the backbone of enterprise software, integrating core business processes including finance, human resources, procurement and manufacturing. ERP software provides a centralized platform that helps coordinate various business units within an organization, improving efficiency and data sharing. Additionally, ERP software integrates supply chains, enhancing visibility, coordination, and overall operational efficiency. These systems provide a single view of business operations and enable data-driven decision making across departments.
Customer relationship management (CRM) software
CRM platforms, equipped with powerful CRM tools, manage customer interactions, sales, and service. The CRM market is projected to be $114.4 billion by 2027.
Business intelligence and analytics tools
These tools provide data analysis, analytics, and reporting capabilities to analyze data, gain insights, and make strategic decisions. They turn data into business intelligence, enabling informed business decisions.
Supply chain management (SCM)
SCM software optimizes logistics, inventory management, and supplier relationships to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Enterprise software use cases and industry applications
Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies use enterprise software to manage complex production processes, inventory control and supply chain operations. For example SaMASZ implemented PLM Windchill to centralize business processes, unify the company’s project infrastructure and close existing solutions in one standardized system.
Healthcare
Healthcare organizations use enterprise software for patient record management, appointment scheduling and compliance tracking. CSIOZ – The Center of Healthcare Information Systems for Ministry of Health. As part of the project people have been given access to user-friendly digital services such as: e-prescription and e-referral, as well as IKP – which is patient’s online account on website pacjent.gov.pl. Ultimately the project also includes implementation of digital medical documentation and medical events register. Digitization of healthcare services is a complex project which requires cooperation of many groups of stakeholders. Its aim is to improve the quality of medical services and their availability in Poland. Initially it has been estimated that around 60% of patients will use the information system being implemented.
Financial services
Financial institutions use enterprise software for risk management, regulatory compliance and customer service. Ernst & Young (EY) has integrated ERP systems to enhance project delivery, resource optimization and client satisfaction.
Retail and e-commerce
Retail companies use enterprise software for inventory management, point-of-sale systems and customer data analytics. Walmart for instance uses SAP S/4HANA alongside Microsoft products for cloud-based enterprise management.
Technology companies
Tech giants like Apple, Google and Microsoft use enterprise software to manage their own operations. Apple has partnered with SAP to leverage SAP S/4HANA for enterprise operations, while Google transitioned from Oracle to SAP for its finance software needs. Oracle software, known for its comprehensive suite of integrated products supporting databases, cloud services, and enterprise management systems, has played a critical role in supporting various business operations for many organizations.
Company profiles: who needs enterprise software?
Large corporations (Fortune 500)
Companies like Starbucks, Amazon and Tesla are the traditional enterprise software market. These organizations need software that can handle millions of transactions, thousands of employees and complex global operations.
Mid-sized growing companies
Organizations with 500-5,000 employees often move to enterprise software as they outgrow standard business tools. These companies need scalable solutions that can adapt to rapid growth and increasing complexity.
Government and public sector
Government agencies and public institutions use enterprise software for citizen services, regulatory compliance and large scale data management.
Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare networks need enterprise software for patient management, electronic health records and regulatory compliance.
Educational institutions
Universities and large school districts use enterprise software for student information systems, financial management and administrative processes.
Enterprise software development lifecycle
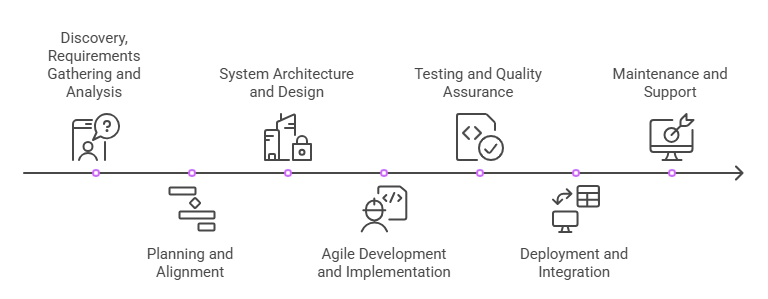
Enterprise software development lifecycle is different from standard software development due to its complexity and scale. Building enterprise software requires a structured, iterative approach balancing robustness with adaptability. The typical process involves seven key phases:
1. Discovery, requirements gathering and analysis
This initial phase involves stakeholder interviews, business process analysis and detailed documentation of functional requirements. Enterprise environments are complex and require thorough understanding of existing systems, user roles and business objectives.
2. Planning and alignment
Enterprise projects require detailed project planning, resource allocation and risk assessment. This phase sets up communication channels, defines roles and responsibilities and creates project roadmaps.
3. System architecture and design
Enterprise software requires robust architectural planning to ensure scalability, security and integration capabilities. This includes database design, API architecture and user interface design.
4. Agile development and implementation
The actual development phase involves coding, module integration and iterative testing. Enterprise projects often use agile methodologies to manage complexity and ensure stakeholder alignment.
5. Testing and quality assurance
Comprehensive testing is critical for enterprise software, including unit testing, integration testing, performance testing and user acceptance testing. By incorporating automation and thorough testing processes, organizations can significantly reduce human error, ensuring greater accuracy and reliability in their software systems.
6. Deployment and integration
Enterprise software deployment requires coordination with existing systems, data migration and user training. Integration during deployment ensures users can access data across various platforms and tools, optimizing workflows and supporting compliance. This phase often involves phased rollouts to minimize business disruption.
7. Maintenance and support
Ongoing maintenance includes regular updates, security patches, performance optimization and user support. Enterprise software requires continuous monitoring and improvement.
Investment requirements and cost considerations
Development costs
Enterprise software development costs vary greatly based on complexity and scope. According to industry data:
- small-scale enterprise software: $100,000-$250,000
- mid-size custom solutions: $250,000-$500,000
- large-scale enterprise platforms: $500,000+
Most custom enterprise software projects fall between $100,000 and $750,000 for complete design, development and implementation.
Implementation and integration costs
Beyond development costs, organizations need to budget for:
- system integration and data migration,
- user training and change management,
- infrastructure upgrades and security implementations,
- ongoing maintenance and support Total Cost of Ownership.
Average ERP implementation cost for mid-sized business: $150,000 – $750,000, $9,000 per user. But what about the operational benefits and ROI?
Market growth and investment trends
Global enterprise software market size: $263.79 billion in 2024, $517.26 billion by 2030, 12.1% CAGR. This growth is driven by increasing recognition of enterprise software as a business investment.
Return on investment and business benefits
Organizations implementing enterprise software see significant ROI:
- operational efficiency: 82% increased operational efficiency,
- cost reduction: 50% manual process time reduction,
- risk mitigation: 30% operational risk reduction,
- performance improvement: 40% fewer data breaches.
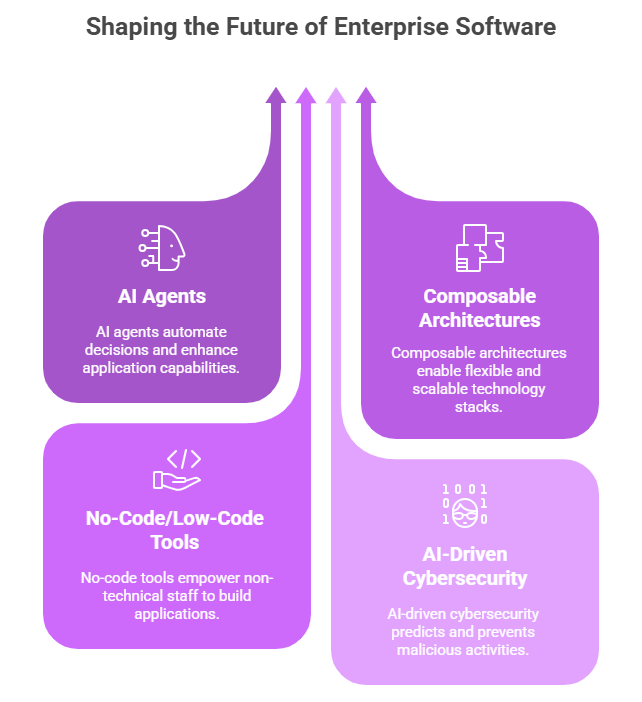
Future trends: AI, composability, and democratization
Enterprise software is evolving:
- AI agents are autonomous or semi-autonomous software entities powered by large language models and other AI technologies. By 2028, 1/3 of enterprise applications will embed AI agents, 15% of all work decisions will be made autonomously.
- Composable architectures allow companies to swap or upgrade components (e.g. CRM or ERP modules) without large-scale rebuilds. MACH – Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native, Headless – enables organizations to tailor and evolve their technology stack.
- No-code and low-code tools (e.g. Microsoft Power Platform) let non-technical staff – “citizen developers” – design, build and automate business apps with minimal or no coding. This democratization reduces IT backlogs, unlocks innovation from business teams and lets professional developers focus on more complex, mission-critical projects.
- AI-driven predictive cybersecurity changes the paradigm from reacting to attacks to preventing them. Advanced machine learning analyzes network traffic, user behavior and historical threat intelligence to predict malicious activity and suggest preventative actions. Platforms use real-time anomaly detection, pattern recognition and predictive modeling to deliver early warnings and strengthen defenses.
Conclusion: more than software, a strategic asset
Enterprise-grade software is a fundamental shift from consumer applications to business solutions for scale, security and integration. As organizations digitize and complexity increases the distinction between standard software and enterprise-grade solutions becomes more important.
The investment in enterprise software – while big – provides the foundation for growth, efficiency and competitive advantage. With the global enterprise software market projected to reach over $500 billion by 2030 the importance of understanding and implementing these solutions will only grow.
For organizations considering enterprise software investments the key is to understand their needs, evaluate solutions on scalability and security requirements and work with experienced development partners who can deliver solutions that meet enterprise-grade standards. The future of business operations depends on making informed decisions about these technology investments.
Enterprise software is a competitive imperative not a luxury. Its value is in scalability, security and efficiency across complex operations. While the initial investment is high – $100K to millions – the ROI in risk reduction, productivity and agility justifies the cost. As platforms evolve to AI-driven, composable models enterprises that adopt these tools will lead in resilience and innovation. The future belongs to organizations that treat software as a support function not the core of transformation
