Smartify your Factory – this journey doesn’t have to be paved with challenges that are too hard to overcome.
Vol.1/3: First steps with Smart Factory
The digital transformation era has come and settled in for good. This includes countless innovations to discover and implement. The recent difficult period has shown that companies must flexibly adapt to new conditions and thus accelerate the adoption of new technologies. Old-school methods no longer work. To stay on top and remain competitive in this rapidly changing landscape, organizations need to adjust their strategies and launch changes quickly, in new ways.
Smartify Factory sounds nice, but seems hard to implement? Don’t worry, it can be quite an interesting adventure as long as you have the right guide on your side.
First things first. Smart Factory – what is it exactly?
To answer this question, we must start with the concept of Industry 4.0, which wasn’t invented yesterday, yet is still unclear to many people. This concept cannot be attributed to a single technology or a single change in the ways of managing production. The fourth industrial revolution is based on the third industrial revolution’s digitalization and automation capabilities. It’s driven by the advancement of the cloud computing and data science and gives a chance to gain insightful information that can solve problems. Once considered unsolvable, today they are achievable by finding patterns that weren’t there before. The merging the digital and physical worlds to build a new virtual one from which the physical world can be managed is enabling changes in the manufacturing industry. This is the way to smart manufacturing and smart factories.
Industry 4.0 aggregates a number of new technologies – incl. Industrial Internet of Things, cloud computing, Big Data analysis, Artificial Intelligence as well as Augmented Reality. The second dimension of Industry 4.0 is related to production management, organizational activities, and the value creation chain.
A change in manufacturing processes is allowed by mentioned above features of Industry 4.0, making flexible yet cost-effective production possible.
The concept associated with Industry 4.0 is Smart Factory – in other words “intelligent factory”. This type of plant is based on integrated systems with the use of the industrial Internet of Things and new methods of production organization. It is intended to enable a high level of product personalization and run production processes with minimal labor input.
The idea and activities within Smart Industry allow companies to shift market competition from offering a simple product to providing value-added products and competing with process excellence. This applies to cooperation with potential customers from the stage of virtual product design, through simulations, production optimization and real-time monitoring, to after-sales service.
Manufacturing objectives have not changed. Focusing on short- and long-term goals & ROI
In the business world, no action should be taken if there is no financial justification or, in the case of investments in infrastructure, it does not bring tangible benefits in the long run. It is no different in the case of the Smart Factory idea. In 2020, according to Forrester Research, 90% of manufacturers considered digital transformation as essential for their success.
Why? Because they believe that the I4.0 initiative will be helpful in achieving their main and well-known objectives:
- Agility of scaling operations (like reduced scrap & rework by 17% and energy usage by 10%)
- Flexibility in product customization
To increase operational productivity & performance (e.g., leverage data that used to be in people’s heads to get to market 20% faster) - To increase manufacturing reliability (e.g., reducing parts inventory costs by 10-15% using integrated business planning)
- To improve Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and enable predictive maintenance to increase uptime
Still, only 12% of companies have achieved digital transformation at enterprise scale. As many as 70% of digital transformations fail. Therefore, it is so important for companies to develop effective digital transformation KPIs.
The implementation of Smart Factory requires changes in processes, and often also their redesign.
This applies, for example, to logistics, production methodology or the creation of feedback between production and R&D, marketing department and customers. As a result, the implementation of the Industry 4.0 concept covers organizations as a whole and requires a strategic approach.
To increase this number, TT PSC suggests starting the digital transition journey to Industry 4.0 in small steps, starting with a pilot production project and identifying short- and long-term goals & ROI.
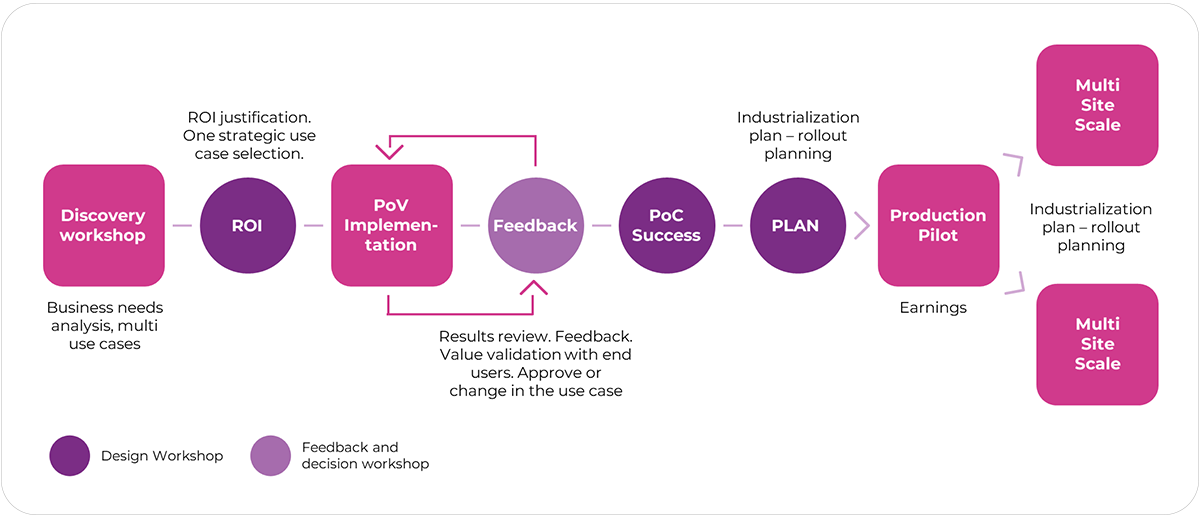
Approach to creating a pilot production path
Pilot projects allow not only to gain knowledge about the usefulness of given technologies, but also to gain first-hand experience in their use. The knowledge gathered during implementation may turn out to be invaluable. When defining the scope of this type of projects, the goals and expected benefits (KPI) should be clearly defined. All projects, not only pilot ones, should be supported by an analysis of four aspects: organizational, staff knowledge and competence, organization of processes and technology.
The next step in the process is the implementation of PoV (Proof of Value – focuses on proving that a given concept will deliver business value and the outcome expected by the customer) based on the knowledge from the previous steps. Full information collected during this process, such as review of results, feedback, validation of value with end-users, approval or changes to the use case, guide us to create an Industrialization Plan and launch a production pilot.
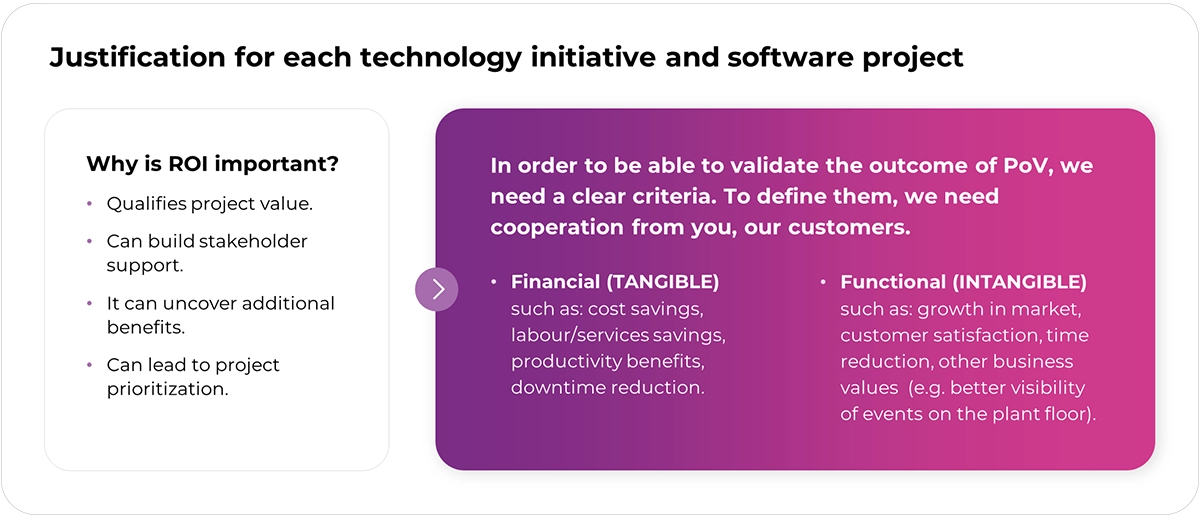
The importance of determining ROI
Full information on resources & needs analysis
Cloud computing and cloud services have been a hot topic for the past few years. There are only a few big players in the market worldwide. One of the major vendors is Amazon with AWS Cloud.
As an emerging technology, it continues to show strong growth, which only proves it is permanent. About 94% of all enterprises use some form of cloud, be it public or private. There are many reasons why cloud computing and AWS Cloud are booming. From its earliest days, the technology was adopted due to the three main pillars of usability – scalability, flexibility, and security.
AWS cloud data storage services have made storing large amounts of data a simple task. This will become more and more useful as we start to take advantage of the achievements, trends and technologies around the Internet of Things, such as Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
Before starting your digital journey, you need to analyze your resources and develop a proper cloud strategy. Good digital transformation KPIs are always correlated to the company’s condition. Once the company sticks a stake in the ground and has a clear direction, then digital transformation will gain the necessary momentum.
The digitization of a factory in the context of Industry 4.0 should be understood as the acquisition of all necessary data on production processes, the machinery condition, inventory, utility consumption, energy costs, production quality, staff availability, the number and lead time of orders, indicators resulting from the company’s market strategy, etc., and parallel processing of these data so as to continuously ensure optimal conditions for the functioning of the enterprise.
Leveraging the power of the AWS cloud and modern technology in general, organizations have enhanced old ways of performing tasks and eliminated redundancies and waste. The game-changer is the AWS cloud’s powerful capability to create change. This is the main enabler and booster of digital transformation.
We work with companies of all sizes to extract knowledge from data and turn it into daily insights using interactive dashboards and reports to gain competitive advantage and increase operational profitability. With the power of the AWS Cloud, we can unleash the potential of all data, enable easy access to it and data analysis across the company. This creates a data-driven culture, and also provides a complete picture of our customers’ business through modern BI solutions. We recommend creating centralized analytics solution to obtain transparent analytics and reporting across the company. Interactive dashboards will help make the right decisions at the right time to improve KPIs and thus control whether a digital journey towards Smart Factory is on the right track.
Assessment of the maturity of Industry 4.0
Depending on the organization, the stage may differ in terms of their digital transformation journey and will have specific requirements that are more relevant to them. Some are still at a very early stage.
In the McKinsey report, over 90% of manufacturers say they are on the same level or ahead of their competitors in the digital transition. However, many companies are still stuck in the pilot stage and face the challenges of moving to the deployment or “scaling” phase.
Manufacturing companies of the future will need to be able to manage their entire value chain in an agile and flexible manner to meet the challenges. They will need virtual and physical structures that allow for close collaboration and rapid adaptation across the entire lifecycle – and across the entire enterprise, from innovation to manufacturing and distribution.
The current state of the art in production technology can be described as being driven mainly by an increase in the efficiency of production processes.
When it comes to the fourth industrial revolution, we understand the maturity of a manufacturing company as the state of advancement of internal and external conditions that support the basic concepts of Industry 4.0. These include vertical and horizontal integration of production systems and enterprises, and digital integration of engineering along the entire value chain.

Main areas to analyze and assess the maturity of Industry 4.0
The ongoing analysis of a company’s position in the digital transformation journey uses several maturity models and related tools to assess the maturity of manufacturing companies’ Industry 4.0.
Determining the maturity level of a manufacturing company on the road to Industry 4.0 is vital to properly developing an action plan – in other words – a roadmap.
Roadmap of the Smart Factory journey
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is transforming manufacturing with the Smart Factory idea. The advanced industrial digital technologies that make up the Industry 4.0 trend are considered the transformative force that will enable this transformation. However, these technologies must be connected, integrated and used effectively to create value and provide visibility for data-driven manufacturing. Smart Factory is a journey and requires a roadmap to guide manufacturing organizations to achieve it.
The illustration below shows the main areas to be addressed on this journey towards Industry 4.0.
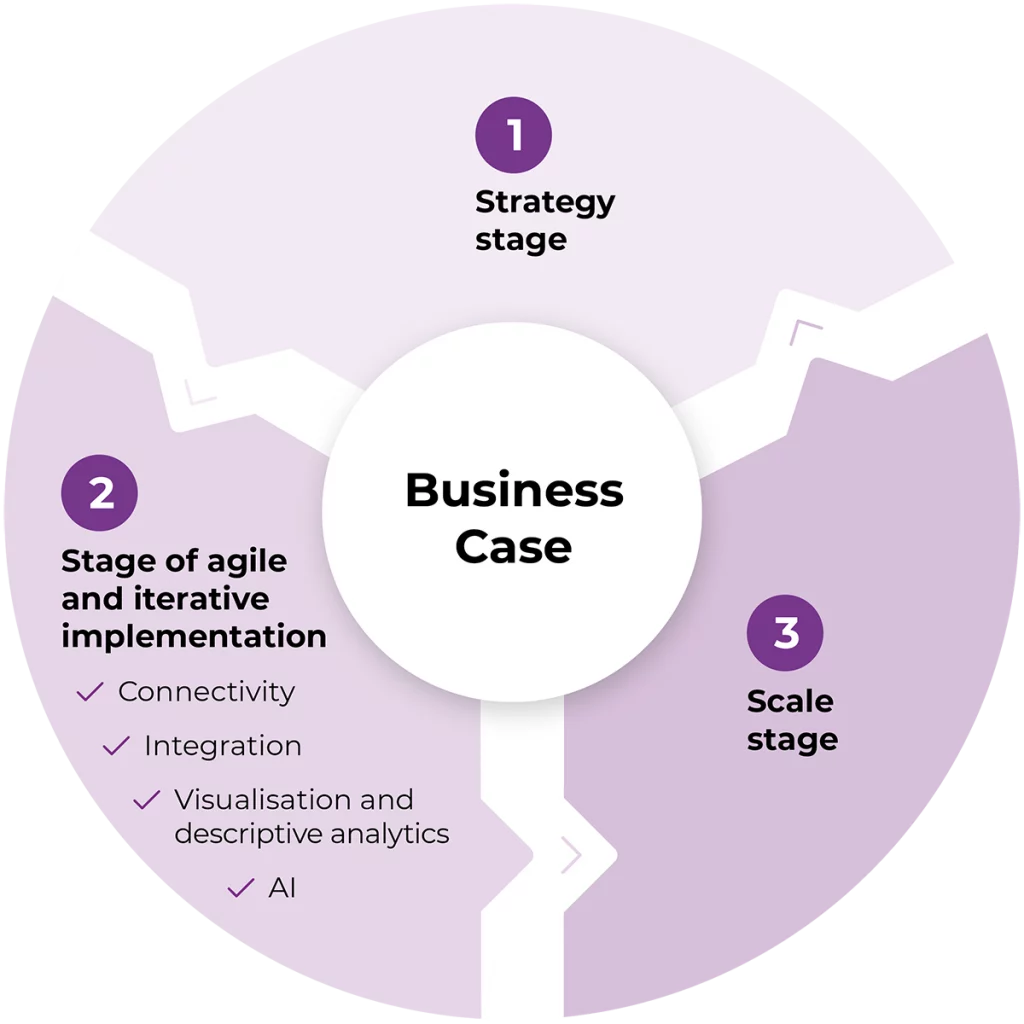
When working with Customers and Partners, we collaborate in order to find appropriate and relevant business cases that bring meaningful value and return. Once assessed and prioritized, these cases build a very specific roadmap that allows for planning the next steps and aligning various stakeholders. The first step is always the strategic one to identify business pain points and problems and define the expected results and the final goal of the initiative. During this phase, a plan to move forward (in the form of the aforementioned roadmap) is created.
The next stage is to execute a set of initiatives, usually in an agile and iterative manner, in order to implement the software component of the transformation. Each project has its own technical and technological areas to be considered, but usually they fit into a couple of standard blocks: Connectivity – determining how to build the foundation of connectivity infrastructure, Integration – assessing the needs and possibilities for integrating required enterprise applications between IT and OT layer, the Analysis and Artificial Intelligence areas – covering analytical tools and methods that can be used to exploit data, turning it into useful information.
The final stage is taking care of scalability, rollout and adoption, which presents various possible approaches that can be used to scale, optimize and further develop the steps of the roadmap throughout your journey to ‘Smartify’ your Factory.
Strategy stage – Identifying the Problem and ROI
Manufacturing organizations have begun to appreciate and take advantage of Industry 4.0, realizing the potential it can offer in terms of improving efficiency, saving costs, and responding to market demands.
As I wrote in paragraph 2, the first step must be a business case with a clear vision, goals and objectives to be achieved that best fits the organization’s business model. This can be done by prioritizing the areas where it will offer the greatest benefits and long-term return on investment (ROI).
In this area, it is crucial to identify and collect real business pain points and assess the degree of their importance, as well as the value of solutions to these challenges and the complexity of implementing changes. In addition, it is also important to analyze the vulnerabities of the current situation / landscape and determine what the desired effect of the plan should be.
The next step is to align the company’s strategy and goals with the cloud strategy. Not forgetting end-user adoption and how these changes will affect their work.
Each manufacturing company can have a different starting point and an individual digital transformation journey. It’s important to identify a specific starting point, understand where you want the value to be created, and start your journey.
Carrying out the stage of agile and iterative implementations
1. Connectivity area
The connectivity on the roadmap is the most important area, as it is the basis on which to build the next areas.
A starting point may be the factory’s IT infrastructure capabilities. Consider having a dedicated IT infrastructure for Industry 4.0 projects, such as an on-premises data center, dedicated AWS cloud infrastructure or a hybrid solution. Each of these has advantages and limitations in terms of cost, maintenance, scalability, reliability, flexibility and security. All these elements should be considered, also taking into account future loads and needs.
Connectivity technologies have become more accessible and affordable due to a significant decline in sensor and computing costs over the past few decades, which has further enabled the advancement of the Internet of Things. The IIoT system is an ecosystem of connected technology elements that collect, store and use data to provide information, trigger events, and recommend actions.
Today, the PLCs and metrics used on the shop floor are more modern, smarter and easier to integrate. However, there is still a huge problem with legacy, old machines – some of which may be decades old – and they have very limited integration capabilities (if at all!).
Cybersecurity is one of the main connectivity challenges in smart manufacturing and also one of the most significant barriers to implementing Industry 4.0. As soon as any device is connected to the Internet, the entire network becomes less secure and resilient if not adequately supported.
2. Integration area
Here we focus on the integration of IT and OT systems in production, which often operate independently. The first one manages business applications from the front office, and the second one ensures the smooth operation of the factory. The integration of IT and OT is the core of smart manufacturing architecture.
There are several key challenges related to the integration phase. They include:
- interoperability (breaking the silos in machines and production equipment that use different languages depending on communication protocols established by suppliers);
- data security (privacy issues with external sources and third-parties in horizontal integration, as this requires data protection and access to it when needed);
- scalability (easy scaling of IT infrastructure by transferring the operation of IT systems to the cloud when the amount and speed of data increases significantly over time);
- adopting cost-effective IT applications (with strong planning and coordination capabilities to handle integration complexity and providing end-to-end visibility with robust data analysis tools).
Industry 4.0 in smart manufacturing includes data extraction from anywhere with minimal connectivity and integration costs, as well as analytical capabilities to provide insight via dashboards that can be accessed from anywhere, including mobile devices or Augmented Reality.
3. Visualization and descriptive analytics area
This area involves analyzing the data collected from various sources of the operational layers of production. Analytics of this data creates value in production by providing a diagnostic approach to underlying troubleshooting problems and providing guidance to reduce production discrepancies. The challenges of dealing with massive amounts of data (Big Data) include the complexity of data processing, data volume, network speed and the bandwidth to process such a large amount of data.
Among the most popular and widespread performance metrics that manufacturing organizations rely on (for operations management), are:
- business’s financial performance (e.g., production cost per unit),
- performance-focused metrics (e.g., factory performance),
- overall equipment efficiency (OEE),
- quality-related indicators (e.g., scrap index, efficiency).
4. AI (Artificial Intelligence) area
The AI area is linked to advanced data analytics and tools to provide new answers to questions posed in the data analysis stage to add real and unexpected value to the manufacturing industry. It is based on the use of Big Data, predictive and forward-looking analytics as well as analytics based on AWS AI.
In the manufacturing industry, AI is a kind of mastermind standing behind the Industry 4.0 transformation. At the same time, other digital technologies are seen as the muscle to support the transition from automation to autonomy.
One of the key applications of AWS AI in combination with IoT is the predictive maintenance of machines, which can significantly reduce repair costs. Artificial intelligence-based learning algorithms detect data trends to provide early warnings and indications of possible malfunctions and failures. This allows for maintenance planning and intervention, leading to a more reliable and sustainable production line.
The use of AI in manufacturing also plays a key role in empowering the workforce with basic knowledge to improve process efficiency and productivity. AI-based algorithms can provide employees with real-time recommendations (using e.g. SkillWorx and Augmented Reality) for tasks, especially for young, inexperienced workers. They can also operate autonomously to solve problems as they arise, making machines adapt to optimize quality or energy efficiency during production operations.
Scale stage
The suggested Roadmap is intended to be dynamic and continuously improved. The sixth process area is therefore related to scalability.
For example, scaling of the strategy phase can be achieved by adding new business cases and initiating in-house projects related to the optimization of processors and procedures in production.
Scaling analytics and AI steps include leveraging available Big Data (such as structured data, unstructured data), relevant analytical methods and Machine Learning tools. This supports deeper and broader applications that add value to the production process.
The best way to get started?
Digital transformation is an interesting journey where you have a chance to test your initiative and its outcomes, as well as learn more about the performance of your business. The essence of the transformation journey is continuous improvement for a better future of your organization.
Being in the department managing the change process puts you at the center of the most important events from the company’s point of view. With reports, you gain confidence that your actions deliver value and thus validate the digital transformation decision.
Accept any challenges with an open mind and focus on achieving relevant and simple KPIs of your digital transformation.



